Biomedical Science & Research Journals | Cost-Benefit Analysis: Hemopatch® Vs Standard of Care in The Incidence of Postoperative Pancreatic Fistula in a Observational Study
Objective: To determine the efficacy and the impact on postoperative morbidity, mortality, and direct hospitalization costs of using the hemostatic-sealant Hemopatch® in patients undergoing pancreaticoduodenectomy.
Method: A retrospective observational data review (26 consecutive pancreaticoduodenectomies) from July 2015 to October 2016 using the same surgical technique, 13 procedures reinforcing the duct-to-mucosa pancreaticojejunostomy with Hemopatch® and 13 procedures without Hemopatch® at Miguel Servet University Hospital, Zaragoza, Spain. Both groups were statistically homogenous. Demographic data and rates of postoperative complications were collected. To extrapolate the average cost for pancreaticoduodenectomy treatment in a larger population with a normal distribution, a Monte Carlo simulation was run with a 1,000-procedure scenario.
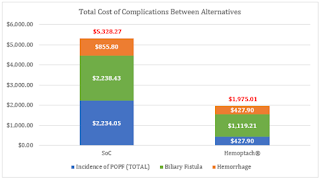
Results: Results of the Monte Carlo simulation determined: the incidence of postoperative pancreatic fistula in the Hemopatch® group reported was 7.7% vs 30.9% (p value: 0.05), biliary fistula 7.7% vs 15.4% (p value: 0.05), hemorrhage 7.7% vs 15.5% (p value: 0.05), mean stay 20.8 vs 26.3 days (p value: 0.01), ICU stay 7.1 vs 9.1 days (p value: 0.01). Therefore, improved outcomes of Hemopatch® vs SoC, respectively resulted in a cost offset of: ICU length of stay $16,254.18 vs $21,000.41, total hospital length of stay $13,659.92 vs $17,233.67 (excluding ICU stay), postoperative pancreatic fistula $427.90 vs $2,234.05 biliary fistula $1,119.21 vs $2,238.43 and hemorrhage $427.90 vs $855.80.
Conclusions: Sealing with Hemopatch® as an adjuvant after a pancreaticoduodenectomy might offer a new possibility to decrease postoperative pancreatic fistula, with fewer severe fistulas, shorter hospital stays and reduced healthcare costs. The use of Hemopatch® resulted in a substantial savings of $10,592.00 (-23%) per patient. Hemopatch® might be an effective and cost-beneficial alternative against the standard of care.
Clinical relevance: The use of Hemopatch® as a sealant may result in better clinical (less morbidity) and possibly economic outcomes in pancreaticoduodenectomy.
To view fulltext of article: hhttps://biomedgrid.com/fulltext/volume1/cost-benefit-analysis-hemopatch-vs-standard-of-care-in-the-incidence-of-postoperative-pancreatic-fistula-in-a-observational-study.ID.000504.php

Comments
Post a Comment