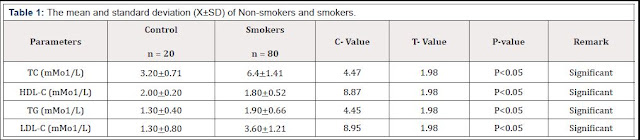
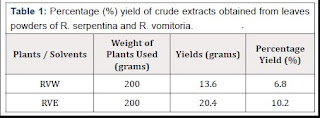
Biomedical Science and Research Journals | Processes of Cultural Change and Health Education
Processes of Cultural Change and Health Education Short Communication In the era of globalisation, the profound technological transformation of production processes is leading to an important change in both the pace of life and time of work, study and leisure. The strong technological acceleration produced by the fastest means of transport, forces us to travel, to run without considering however the impact of our way of travelling on the environment and on the quality of life in our city. In an ever more interconnected world, which changes with extraordinary rapidity and speed, it becomes urgent to reflect on phenomena that we usually define synthetically with the industry 4.0 [ 1 ]. How do we educate ourselves in these profound changes? How to question the opportunities that new generations will have to make a great contribution to human and sustainable development in the future of society. If in the time of St. Jerome the language was latin today is the “digital”, the language ...